Power Supply Glossary Term For AC, DC, Voltage, Current And Many More.
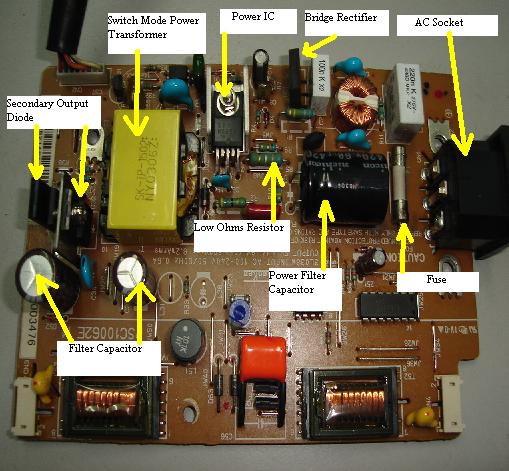
A Switch Mode Power Supply Board
AC (Alternating Current) – A current that periodically reverses its direction of flow. The electricity supply to homes, offices, factories and etc. is AC.
AC Line – A power line that delivers alternating current only.
AC Line Filter – A filter designed to remove extraneous signals or electrical noise from an AC power line, while causing virtually no reduction of the power line voltage or power.
AC Line Voltage – The voltage commonly delivered by the commercial power line to consumers. In the United States, the two standards are 117V and 234V (~ about 5 percent). The lower voltage is used by most appliances; the higher voltage is intended for appliances and equipment that draws high power, such as electric ovens, cooking ranges, clothes dryers, and amateurs-radio amplifiers. In Europe, 220V is the common standard.
AC Noise – Electromagnetic interference originating in the AC power lines or electrical noise of a rapidly alternating or pulsating nature.
Bleeder- A resistor or group of resistors, used permanently to drain current from charged capacitors. It establishes the predetermined initial load level for a power supply or signal source, and it serves a safety device in high voltage power supplies.
Crest Factor - This is the ratio between the peak current and the average current required by the load. Computers normally exhibit a crest factor of 2 to 3, which means the computer draws two to three times the average current for short duration, such as the starting time etc.
Current - It is a quantitative measure of the amount of electricity passing through a circuit or the movement of charge carriers, such as electrons, holes, or ions. The unit for measuring the current is Amperes.
Current Limiting – The controlling of current so that it does not exceed a desired value.
Current Limiting Resistor- A series resistor inserted into a circuit to limit the current to a desired value.
Current Meter – A normally direct-reading instrument, such as an ammeter, milli ammeter, or micrometer, used to measure current strength.
Current Noise – Electrical noise produced by current flowing through a resistor.
DC (Direct Current) - It has either a positive or negative polarity and flows in one direction. A DC charge can be stored more easily and is used for all batteries.
DC Power Supply – A power unit that supplies direct current only. Examples: battery, transformer / rectifier / filter circuit, DC generator, and photovoltaic cell.
DC Voltage- A voltage that does not change in polarity, an example being the voltage delivered by a battery or dc generator.
DC Working Voltage- The rated dc voltage at which a component can be operated continuously with safety and reliability.
Impedance - It is combination of resistance, inductance and capacitance which restricts the current through any device.
Inverter - It is a circuit which converts DC to AC.
Line Loss- The sum of energy losses in a transmission line.
Line Noise- Electrical noise (as received by a radio) arising from fluctuations of current or voltage in a power line.
Power Factor - This is the ratio of real power to apparent power (VA/watts). The power factor can be ‘leading’ or ‘lagging’ depending upon the type of load. Inductive loads cause the current to lag and capacitive loads causes the current to lead the voltage.
Power Factor Meter – An instrument that gives direct readings of power factor (lead or lag). One such meter uses a dynamometer-type movement in which the rotating element consists of two coils fastened together at right angles.
Power Line Frequency- The frequency of the alternating current and voltage available over commercial power line. In the United States, the power frequency is 60 hz while some countries is 50 hz.
Power Rating – The specified power required by equipment for normal operation.
Power Supply – A device, such as a generator or a transformer-rectifier-filter arrangement, that produces the power needed to operate on electronic equipment.
Power Surge- A momentary increase in the voltage on a utility line.
Power Switch- The switch for controlling power to a piece of equipment.
Power Transistor – A heavy-duty transistor designed for power-amplifier and power-control service.
PWM - Pulse Width Modulation is a technique employed to regulate the output power by changing the pulse width. PWM is employed is SMPS, UPS and many other power control applications.
Rectifier - It is a diode network which changes AC to DC. This is reverse of a inverter which converts DC to AC.
Ripple- A small alternating current component in the output of a direct current power supply with inadequate filtering.
Sine Wave - It is the most simple of all wave forms and is the shape of the AC in homes, offices etc. In a sine wave, the voltage or current changes smoothly from a negative maximum to a positive maximum with changing time.
Square Wave - This waveform is similar to the sine wave except that the transitions from negative maximum to positive maximum are abrupt. Most domestic invertor’s supply a square wave as it is simple to generate.
Surge Suppressor. A semiconductor device used to absorb potentially destructive transients or over voltages on a utility power line.
Transformer - A device used to convert an AC voltage to different AC voltage levels. A transformer is also used to isolate the output AC power from the source.
Transient- A sudden high voltage spike in an alternating current system, caused by arcing or lightning
VA (Volt Ampere) - This is the simple product of voltage and current and is used to express the amount of power. VA gives the apparent power.
Voltage - It is a measure of the potential difference between two points, it is what causes the current to flow from a higher potential. This is measured in volts.
Voltage Breakdown-The voltage at which current suddenly passes in destructive amounts of dielectric.
Wattage - This is a measure of energy drawn per second by the load. It is calculated by multiplying the VA by the power factor (VA x pf). This gives the true power. The pf varies between 0 for ideal inductive and capacitive loads to 1 for pure resistive loads (incandescent lamps). The pf for a typical computer would be between 0.6 and 0.8 in most cases.
Wattmeter- An instrument used to measure electrical power. The scale usually reads directly in watts, kilowatts, milliwatts, or microwatts.
Wave Form - This is the name given to the shape followed by any alternating current or voltage.
Winding- A coil in an inductor or transformer such as the primary and secondary winding.
If you came across my articles that have some terms you don't understand, just drop by this page of power supply glossary term and hope you can find the meaning you are looking for.
|
|
Copyright@ 2006-2014-www.ElectronicRepairGuide.com All Rights Reserved